Introduction: The Man Behind the Fortune
Elon Musk net worth 2025 stands at a staggering $700 billion, making him the wealthiest person on Earth. But the numbers tell just half the story. Behind the uncolored valuations lies a lifetime of risk, rejection, resilience, and ruthless ambition—a journey that transformed a bullied kid in South Africa into the architect of humanity’s future.
According to his latest estimates, Elon Musk’s net worth in 2025 has been propelled by Tesla’s dominance, SpaceX’s unprecedented success, and strategic bets on AI, renewable energy, and space colonization. Yet Musk didn’t inherit this fortune. He built it from nothing, surviving near-bankruptcy multiple times while reshaping entire industries.
This is the extraordinary story of how one man’s vision created a $700 billion empire—and what it means for the rest of us.
The Boy Who Didn't Belong
Elon Musk wasn’t born into privilege or power. Growing up in Pretoria, South Africa during the 1970s and 80s, he was the weird kid—socially awkward, obsessed with books, perpetually lost in thought. He didn’t just struggle to fit in; he was brutally bullied. Once, a group of boys threw him down a flight of stairs and beat him so badly he was hospitalized.
But the isolation became his superpower. While other kids played outside, Musk devoured encyclopedias and taught himself computer programming at age 10. By 12, he’d created and sold his first video game—a space-themed shooter called Blastar—for $500. It wasn’t just precocious talent; it was an early glimpse of his refusal to accept the world as it was.
At 17, Musk left South Africa to avoid mandatory military service and chase bigger dreams. With barely any money, he bounced between odd jobs in Canada, sometimes sleeping in his car. The comfortable narratives we tell about “self-made” billionaires rarely include this part—the years of uncertainty, the humbling survival jobs, the quiet desperation masked by relentless ambition. For Musk, these weren’t just obstacles. They became foundational to everything that followed.
The Leap Across Continents: Building Foundations in North America
Musk’s first real taste of success came not from rockets or cars, but from the internet gold rush of the late 1990s. After transferring to the University of Pennsylvania and earning degrees in physics and economics, he was accepted into Stanford’s PhD program. He lasted exactly two days before dropping out to launch a startup.
That company, Zip2, was a clunky online city guide for newspapers—think pre-Google Maps meets Yelp. Musk coded obsessively, often sleeping under his desk and showering at the YMCA. When Compaq bought Zip2 for $307 million in 1999, Musk walked away with $22 million at age 27. Most people would retire. Musk immediately started another company.
X.com—which would later become PayPal after a turbulent merger—revolutionized online payments. But success came with chaos. Board conflicts led to Musk being ousted as CEO while he was on his honeymoon. When eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk pocketed $180 million. He was 31, newly wealthy, and determined to tackle problems that “really mattered to humanity.”
The First Fortune: Coding, Coffee, and the Seed of an Empire
By 2002, most dot-com millionaires were buying yachts or retiring early. Musk did something different: he invested nearly everything into two impossibly risky ventures that industry experts said would fail.
The first was SpaceX. After being rejected by established aerospace companies who laughed at his ideas, Musk founded his own rocket company with a audacious goal—make humanity a multi-planetary species. Critics called it a billionaire’s vanity project. Former NASA engineers warned the money would evaporate on the launchpad.
The second bet was even stranger. In 2004, Musk invested in a tiny electric car startup called Tesla, eventually taking control as chairman and later CEO. The auto industry dismissed electric vehicles as impractical toys. Detroit executives mocked the idea that a tech entrepreneur could compete with century-old carmakers.
Musk wasn’t deterred. He’d survived childhood beatings, bankruptcy scares, and boardroom coups. This was the period that would define Elon Musk’s net worth 2025 trajectory—not through safe investments, but through calculated gambles on humanity’s future.
The Edge of Oblivion: Rockets, Cars, and Collapse
By 2008, Musk was staring into the abyss. Both SpaceX and Tesla were hemorrhaging cash. Three SpaceX rocket launches had failed spectacularly—$90 million literally exploding on the launchpad. Tesla’s Roadster faced production nightmares. The 2008 financial crisis crushed investor appetite for risky ventures.
Musk had a choice: save one company or watch both die. He didn’t choose. Instead, he scraped together every dollar—selling assets, borrowing from friends, maxing out credit cards—and bet it all on both companies. He had enough money for one more SpaceX launch.
On September 28, 2008, SpaceX’s fourth Falcon 1 rocket roared into orbit. It was the first privately funded liquid-fuel rocket to reach space. NASA noticed. Within weeks, they awarded SpaceX a $1.6 billion contract for cargo delivery to the International Space Station. Tesla, meanwhile, secured a Department of Energy loan that kept the lights on.
Musk later admitted he gave both companies about a 10% chance of success. The fact that Elon Musk net worth in 2025 now exceeds $400 billion traces directly to this moment—when he refused to accept failure as inevitable.
The Rise of a New Industrial Age: SpaceX Takes Flight
SpaceX didn’t just survive 2008—it rewrote the rules of aerospace. By perfecting reusable rockets, Musk slashed launch costs from $200 million to under $30 million per mission. What had been NASA’s exclusive domain became a competitive marketplace.
The breakthrough came in 2015 when a Falcon 9 first stage landed vertically after delivering satellites to orbit. Engineers wept. Competitors scrambled. Traditional aerospace giants like Boeing and Lockheed suddenly looked outdated.
By 2020, SpaceX was launching astronauts to the International Space Station—the first private company to do so. The Starlink satellite constellation began beaming internet to remote corners of Earth. Starship, the massive fully-reusable rocket designed for Mars missions, moved from fantasy to hardware testing.
SpaceX is now valued at over $200 billion, making it the world’s most valuable private company. Musk owns roughly 42% of it, adding approximately $80-90 billion to Elon Musk’s net worth in 2025. But the financial success was never the primary goal. “I didn’t expect SpaceX to succeed,” Musk once said. “I just thought it was important enough to try.”
Tesla: From Skepticism to Domination
While SpaceX was conquering space, Tesla was transforming transportation. The Model S, launched in 2012, wasn’t just an electric car—it was a computer on wheels that happened to have stunning acceleration and cutting-edge software.
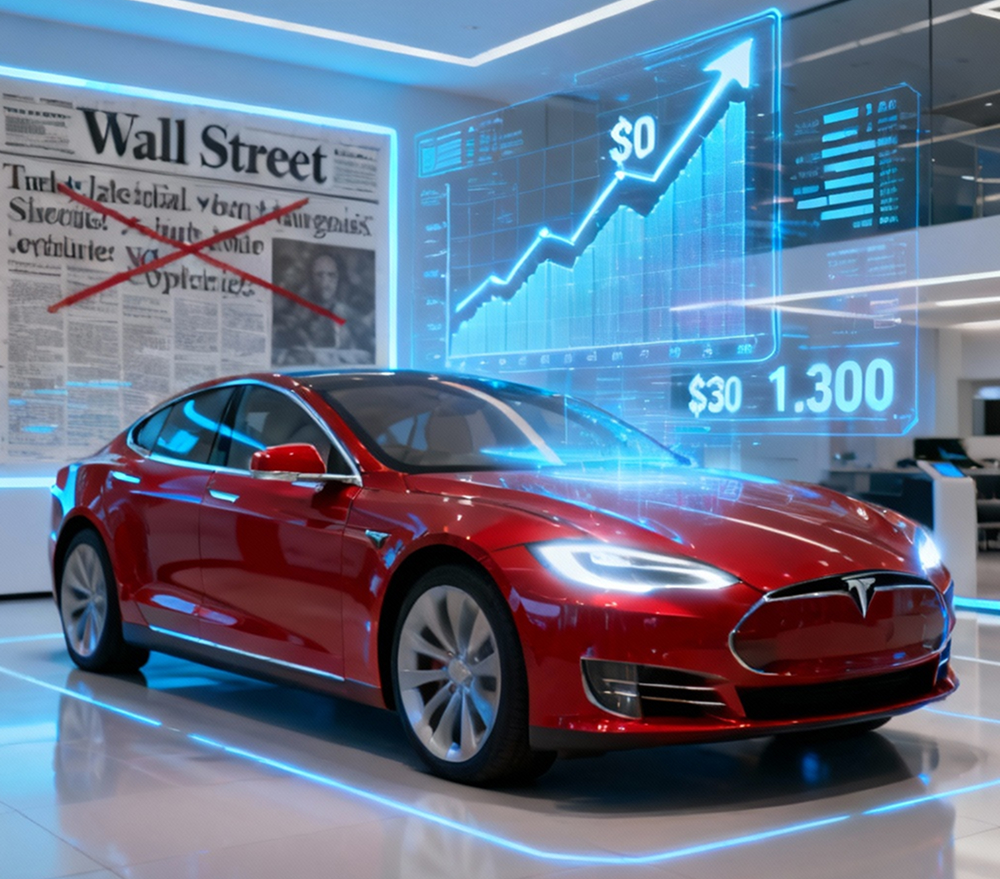
Wall Street remained skeptical for years. Short-sellers bet billions that Tesla would collapse. Musk faced constant production crises, executive departures, and SEC investigations over his chaotic Twitter usage. The company teetered on bankruptcy multiple times.
Then came the Model 3. Despite a painful “production hell,” Tesla delivered an affordable long-range EV that ordinary buyers actually wanted. Sales exploded. Legacy automakers, who’d spent decades dismissing electric vehicles, suddenly announced frantic plans to go electric—validating Musk’s decade-long insistence that the future was battery-powered.
By 2025, Tesla will dominate the EV market with roughly 20% global market share. The company’s market cap hovers around $1.3 trillion, with Musk’s 13% stake contributing approximately $170 billion to his net worth. Tesla proved that one entrepreneur with a stubborn vision could force an entire industry to change course.
The AI Awakening and the Existential Question
In 2023, Musk launched xAI, positioning it as a rival to OpenAI (which he co-founded but later left over philosophical differences). His stated mission: develop “truth-seeking AI” that understands the universe rather than simply maximizing engagement or profit.
Critics accused him of hypocrisy—warning about AI dangers while simultaneously building AI systems. Musk’s counterargument was characteristically blunt: since AI development is inevitable, humanity needs diverse approaches, not a monopoly controlled by a few tech giants.
Whether xAI succeeds remains uncertain, but it reflects Musk’s pattern: identify what he considers humanity’s biggest risks and opportunities, then build companies to address them, regardless of conventional wisdom or personal cost.
Tesla's Future: Robots, Autonomy, and the Next Trillion
Tesla’s ambitions now extend far beyond electric cars. The company is betting big on three revolutionary technologies that could multiply Elon Musk net worth 2025 even further.
Optimus, the Humanoid Robot: Unveiled in 2022, Tesla’s humanoid robot initially drew skepticism. But by 2024, improved prototypes demonstrated the ability to perform factory tasks, sort objects, and navigate complex environments. Musk envisions mass-producing millions of units to address labor shortages in manufacturing, caregiving, and dangerous jobs. If successful, the robotics market could eclipse automotive entirely.
Full Self-Driving Technology: Tesla’s FSD remains both a technological marvel and a persistent controversy. Despite years of “next year” predictions for true autonomy, the system has improved dramatically through billions of real-world driving miles. Musk claims FSD could transform Tesla’s business model—turning every vehicle into a potential robotaxi. Regulators remain cautious, but the technology inches closer to viability.
The Energy Empire: Beyond vehicles and robots, Tesla’s energy division has quietly become a multi-billion dollar business. Powerwall home batteries, Megapack grid storage, and Solar Roofs position Tesla at the center of renewable energy infrastructure. As production costs fall and adoption accelerates, this division could become as valuable as the automotive business.
These three pillars—robotics, autonomy, and energy—represent Musk’s bet that Tesla isn’t just a car company but a diversified technology and energy conglomerate.
The Long Road to Mars: SpaceX's Interplanetary Mission
Musk’s ultimate goal has never wavered: to make humanity a multi-planetary species. SpaceX’s Starship—the largest and most powerful rocket ever built—is designed to carry 100+ people to Mars and return fully reusable.
In 2025, Musk launched xAI, positioning it as humanity’s “truth-seeking” AI alternative. The company raised billions and released Grok, an AI chatbot with fewer content restrictions than competitors. Whether xAI becomes a major player or another Musk side project remains to be seen, but it reflects his pattern of identifying existential challenges and building companies to address them.
The technical challenges are staggering: life support systems, radiation protection, in-situ resource utilization, and establishing a self-sustaining colony millions of miles from Earth. Critics call it science fiction. Musk calls it insurance against extinction-level events—whether from asteroid impacts, nuclear war, or runaway climate change.
SpaceX has already secured NASA contracts for lunar missions and is developing technologies that could enable Mars colonization within the next two decades. Whether humans actually reach Mars in Musk’s lifetime is uncertain, but SpaceX has already fundamentally changed what’s considered possible.
Tesla, Robots, and the Race to a Trillion
Few modern figures polarize like Elon Musk. Admirers see a visionary pushing humanity forward through sheer force of will. Detractors point to broken promises, erratic behavior, workplace controversies, and a management style that prioritizes results over empathy.
Both perspectives contain truth. Musk has accelerated electric vehicle adoption by at least a decade, revolutionized space access, and forced entire industries to innovate faster. He’s also faced lawsuits over working conditions, been fined by the SEC for misleading tweets, and cultivated a public persona that swings between brilliant engineer and internet troll.
His acquisition and transformation of Twitter into X exemplified this duality. Musk claimed he was defending free speech and combating censorship. Critics argued he was enabling harassment and misinformation while running a social media platform into the ground. User engagement dropped, advertisers fled, yet Musk seemed indifferent to conventional business metrics.
The question isn’t whether Musk is likable—it’s whether his contributions outweigh his controversies. History will likely judge him not by his tweets but by whether his companies actually solved the problems they promised to address.
Lessons from Elon's Playbook: What the Rest of Us Can Learn
Beyond the billions, Musk’s journey offers insights for anyone trying to build something meaningful:
Embrace Failure as Tuition: Three exploded rockets didn’t stop SpaceX. Multiple Tesla “production hells” didn’t shut down the company. Musk treats failures as expensive lessons, not endpoints.
Bet on Long-Term Thinking: Electric cars weren’t profitable in 2004. Reusable rockets seemed impossible in 2002. Musk built companies based on where technology would be in 20 years, not where it was then.
Question Every Assumption: Why do rockets have to be disposable? Why can’t cars be software platforms? Musk’s breakthrough successes came from refusing to accept “that’s how it’s always been done.”
Work at the Limits of Human Capacity: Musk’s 80-100-hour workweeks and demand for similar intensity from employees are controversial, but they reflect his belief that changing the world requires extreme effort.
Think in First Principles: Rather than reasoning by analogy, Musk breaks problems down to fundamental truths and rebuilds solutions from scratch. This approach led to cost reductions that legacy companies insisted were impossible.
Whether you admire or despise Musk, his playbook demonstrates that individual agency still matters in shaping the future.
The Extraordinary Legacy of Elon Musk
Elon Musk net worth 2025 may be measured in hundreds of billions, but his real legacy lies elsewhere. He forced the automotive industry to embrace electrification. He proved that private companies could access space more efficiently than governments. He made renewable energy and battery storage economically viable at scale.
Few individuals in history have impacted so many industries simultaneously. Love him or hate him, Musk expanded humanity’s sense of what’s achievable. He demonstrated that one person with capital, vision, and relentless execution can bend entire sectors to their will.
The bullied kid from South Africa who taught himself programming didn’t just get rich—he rewrote the rules of what entrepreneurs could attempt. Whether his companies ultimately deliver on their most ambitious promises (Mars colonies, autonomous transportation, humanoid robots) remains uncertain.
But Musk has already secured his place in history. Not as the world’s richest person, but as the entrepreneur who convinced millions that the future didn’t have to be incremental—it could be revolutionary. And that might be worth more than $700 billion.
Epilogue: The Distance Between Earth and Mars
Because somewhere in a factory, a rocket is being assembled that might one day carry humans beyond Earth. In a laboratory, engineers are training robots that could redefine labor. On roads worldwide, electric vehicles are displacing internal combustion engines that dominated for a century.
Elon Musk didn’t build his $700 billion empire by playing it safe. He built it by asking uncomfortable questions about humanity’s future and risking everything on his answers. Whether those answers prove correct will determine not just Elon Musk’s net worth in 2025 and beyond, but potentially the trajectory of human civilization itself.
In 2025, when analysts debate whether Musk’s companies are overvalued or whether his predictions will materialize, they’re really asking: How much are bold visions worth? And can one person’s obsession change the world?
The numbers say $700 billion. But the real answer won’t be known for decades—perhaps not until humans actually walk on Mars, or humanoid robots become commonplace, or the last gasoline car rolls off an assembly line.
Musk once said counting money is like counting the score in a video game. What matters is the game itself—and whether humanity survives and thrives into the far future. That’s the extraordinary legacy of a kid who refused to accept the world as it was, and spent a lifetime building the world he thought it should become.
“All images in this article were generated using AI tools for illustrative purposes. They are designed to visualize concepts and should not be considered actual product photographs.”